Introduction
Financial Accounting is an area of accounting that considers cash or other monetary items as a basis for the determination of performance rather than as a determinant of production. In the financial accounting process, accounting data or information is classified as cash inflow and outflow in terms of revenue and expenditure, assets, and liabilities. Financial data and information are collected and then summarised to prepare financial statements, income statements, cash flows, and changes in equity for reporting purposes (Edwards, 2013). In financial accounting, the main motive of the organization is to present financial data and information systematically for users of financial data, such as investors, relevant authorities, lenders and creditors, debtors, etc. This report describes the purpose of financial accounting, regulations concerned with financial accounting, rules and principles of accounting, and different aspects of financial reporting, including concepts and conventions related to consistency and material disclosure.
BUSINESS REPORT
1. Define Financial Accounting and Its Purpose
Financial accounting refers to a set of activities related to the preparation of financial statements to present or report financial performance and position to internal or external users of financial data. Major activities of financial reporting include recording, classifying, summarising, posting, analyzing, and reporting financial data or information of business organizations, including drafting financial statements such as balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow analysis. Financial accounting not only covers monetary items but also non-monetary items which assist in reporting purposes. Financial accounting starts with the collection of financial data and information and ends with the reporting of financial performance and position (Fourie, 2015). In the financial accounting process, accounts are prepared by local and international accounting assumptions and standards. The following points describe the purpose of financial accounting and are discussed below:
- The primary purpose of financial accounting is to report final accounts to external or internal.
- Financial accounting assists in compliance with rules and regulations prescribed by relevant authorities.
- Financial accounting through internal checks ensures accuracy in the recording of financial information and data.
- It assists in the identification of suitable accounting policies, assumptions, conventions, and other fundamentals as per the business structure of the organization.
- Financial accounting provides a basis for choosing and implementing the most appropriate strategy as per business requirements.
- Actual outcomes regarding financial performance and position of the business organization under the financial accounting process define the objectives and goals of the company.

2. Regulations Related to Financial Accounting:
Regulations refer to steps normally in the form of order, taken by relevant authorities or governing bodies to control and regulate the activities of organizations or individuals. To establish proper control and to maintain uniformity in accounts, relevant authorities create regulations. The following are the significant regulations relating to financial accounting:
- Regulations guide the preparation and presentation of financial accounts, such as generally accepted accounting policies and standards.
- Some regulations are applicable for organizations operating their businesses globally, such as IFRS (International Financial Reporting Framework).
- For uniformity in the financial accounting process, some regulations are framed regarding accounting assumptions, concepts, methods, conventions, and policies (Hale and Held, 2012).
- For business organizations regulated under any specific act, regulations are framed under such relevant act.
3. Describe Accounting Rules and Principles
Data and information are initially recorded using accounting entries. There are some accounting rules are discussed below which help the organization to smooth its financial accounting process:
Debit what comes in, credit what goes out: This rule is mainly framed for real accounts. Real accounts include all assets of a firm, whether tangible or intangible, such as plant and machinery accounts, furniture and fixtures, goodwill, land and building accounts, free-hold premises, etc. Real accounts are classified as Tangible real accounts and Intangible real accounts. Tangible real accounts include building accounts, plant accounts, inventory accounts, etc. Whereas Tangible real accounts include accounts of items that do not have any physical existence, such as goodwill, patents, copyrights, etc.
Debit the receiver, credit the giver: This rule is framed for personal accounts. A personal account refers to a general ledger account concerned with individuals, firms, and associations like creditors' accounts, debtors accounts, capital accounts, bank accounts, etc. Under this rule, if a person gives something to an organization, it is treated as an inflow; therefore, a personal account will be credited and if a person receives something from the organization, then the amount should be debited in the name of the person (Hall, 2012).
Debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains: This rule is framed for a nominal account. A nominal account refers to a general ledger account concerned with all revenues or income, expenses, losses, and gains. In this rule, capital is treated as liability for business and liability shows credit balances. Incomes and gains lead to an increase in capital; therefore, all incomes and gains are credited, whereas all expenses and losses should be debited because expenses or losses lead to a decrease in capital.
Principle the following are the major principles of accounting that provide a framework for the preparation of final accounts, as follows:
Dual aspect concept: The dual aspect concept truly resembles a double-entry system. According to the dual aspect concepeveryery transaction in a business organization affects both the debit and credit side simultaneously. Under a Single-entry system, only one side of an account is affected, which creates complexity in accounting calculation; therefore, a single-entry system is avoided by entities (Jönsson, 2013).
Cost principle: This principle emphasizes reporting assets on their cost. As per this principle, business organizations should record their assets on actual cost.
Matching principle: According to this principle, all expenses of a business should be matched with revenues that occur or are occurring in a particular period.
4. Conventions and Concepts Relating to Consistency and Material Disclosure
Accounting convention refers to guidelines and frameworks for the adoption of accounting principles. It includes general practices and guidelines which assist in the preparation of final accounts. Accounting conventions are used in areas where no accounting standard is prescribed. Conventions are applied by business organizations as per their requirements to reduce complexity in the accounting process (Mullinova, 2016).
Convention of consistency: Conventions of consistency emphasize maintaining consistency in applied policies and assumptions from period to period. The use of this convention assists in the preparation of comparative accounts and reduces complexities in the accounting process.
Convention of material disclosure: This convention creates uniformity in the disclosures of material items in different organizations. Disclosure of material items in final accounts helps to identify any fraud, error, or irregularity in a business organization.
CLIENT 1
(a) Journal Entry in the Books of David:
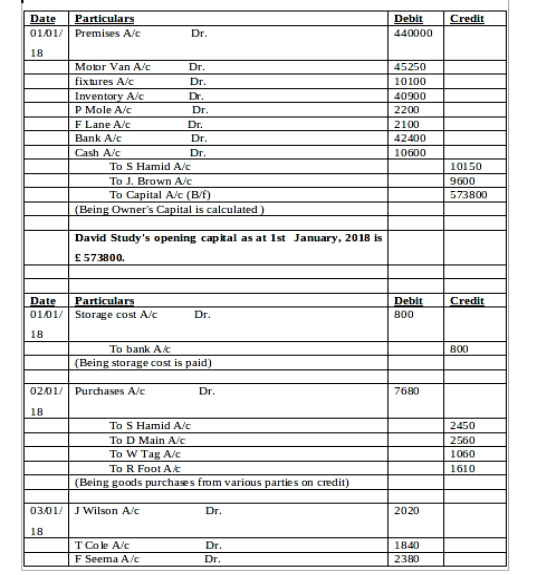
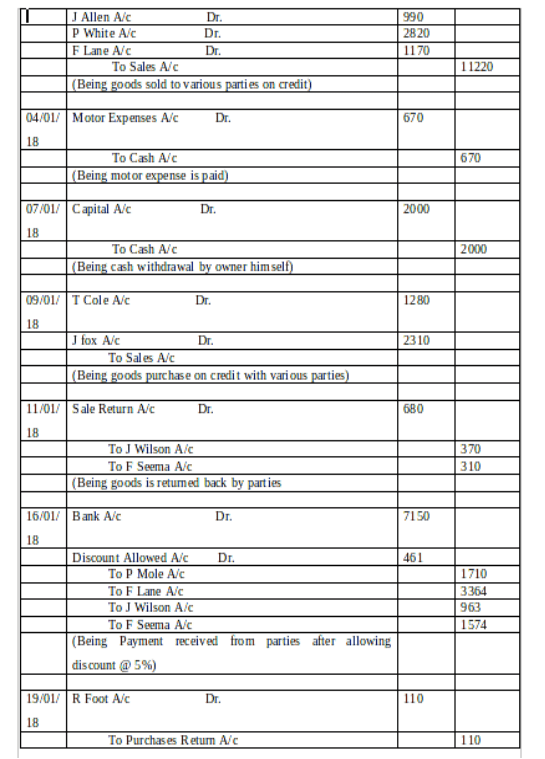
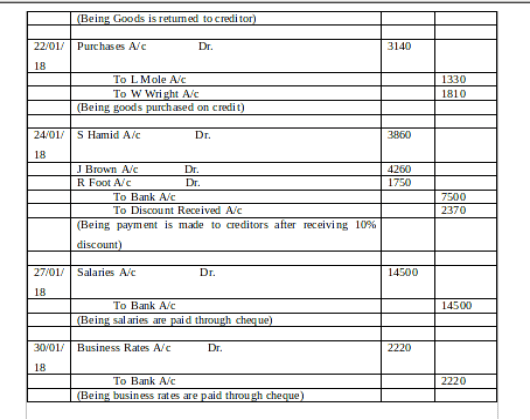
(b) Ledger Accounts:
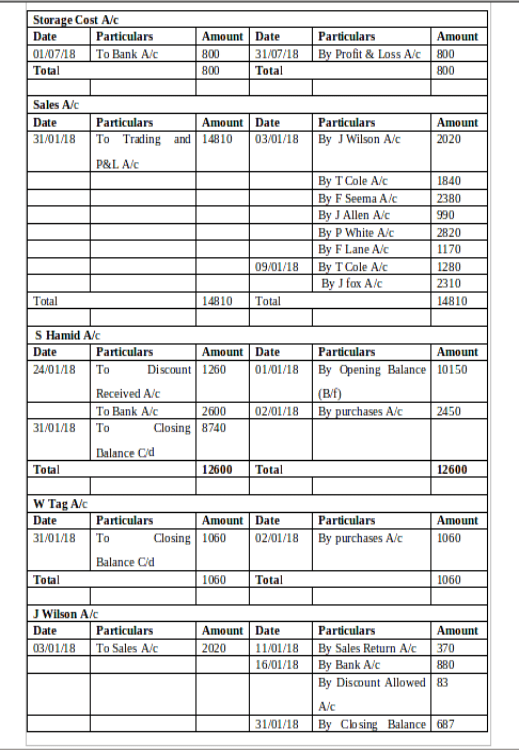
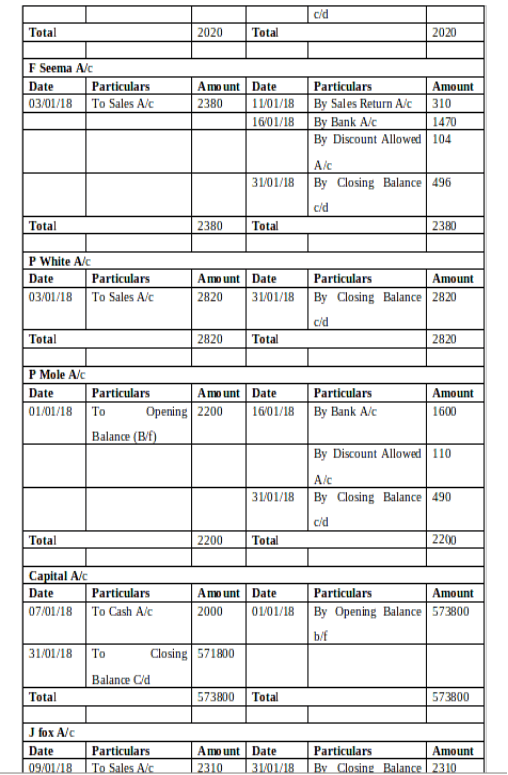
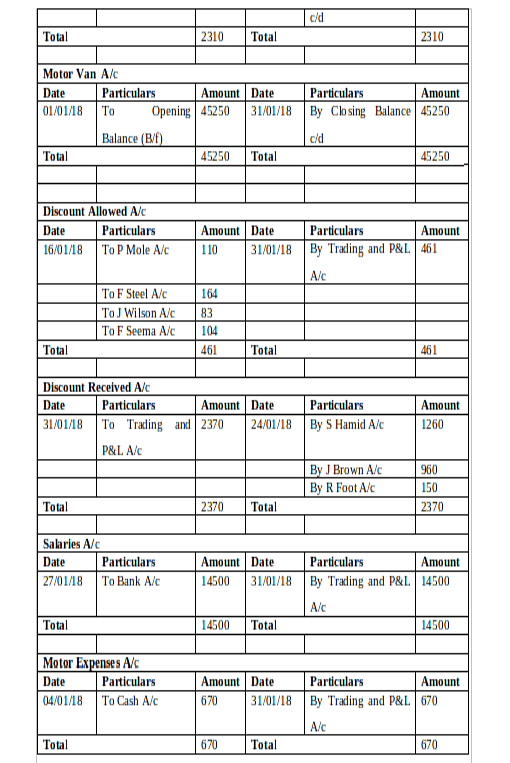
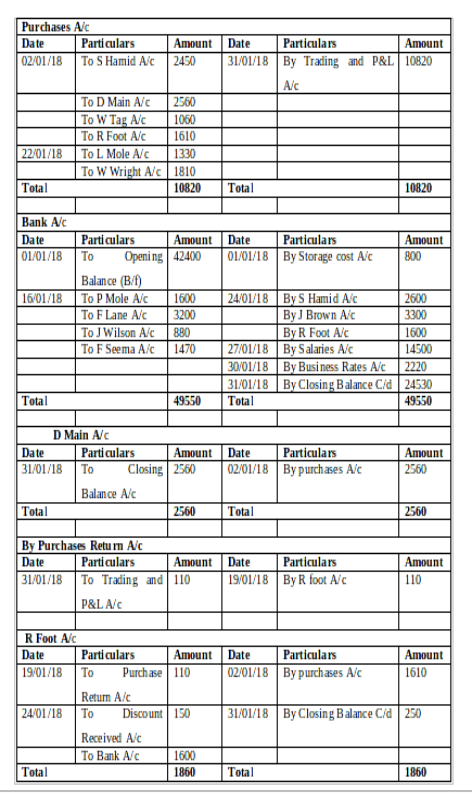
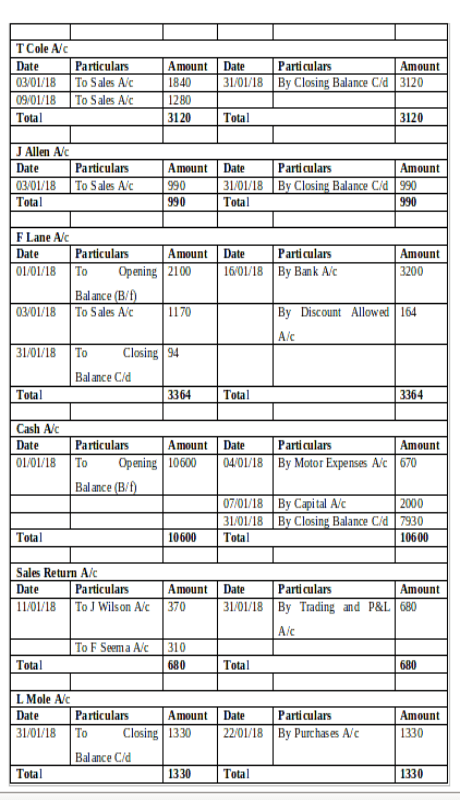
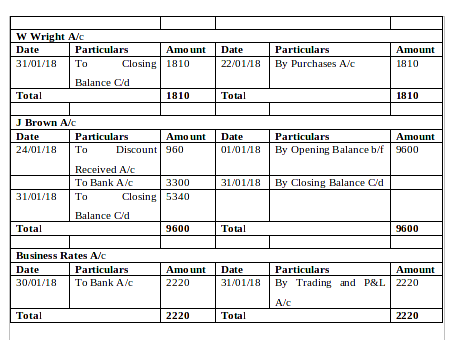
(c) Trial Balance as of 31st January 2018:
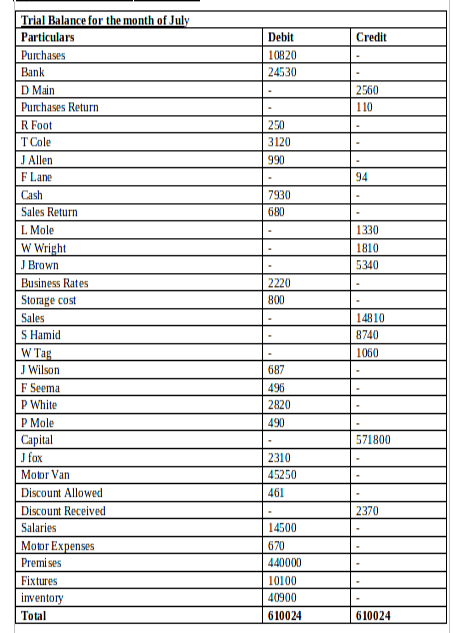
CLIENT 2
(a) Statement of Profit and Loss for Peter Hampau for the Year Ended 31st July 2018
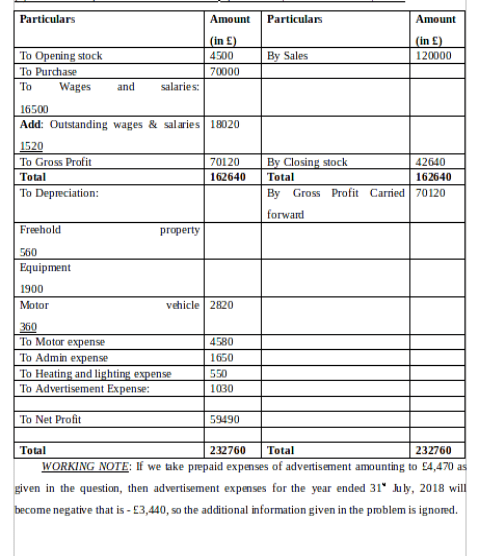
(b) Statement of Financial Position for Peter Hampau as of 31st July 2018
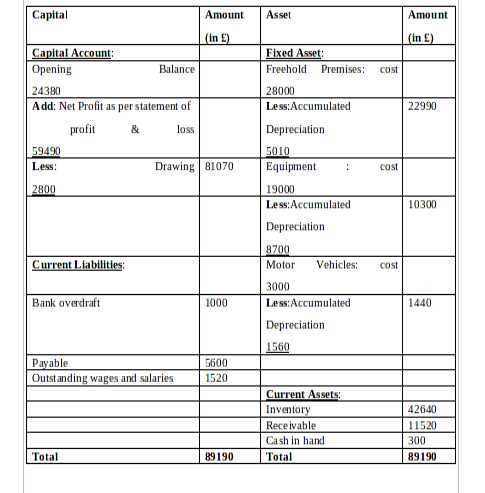
CLIENT 3
(a) Profit and Loss Account of Bowling Limited:
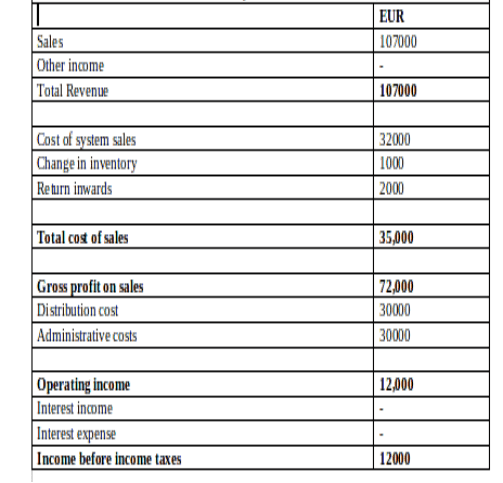
(b) Balance Sheet of Bowling Limited
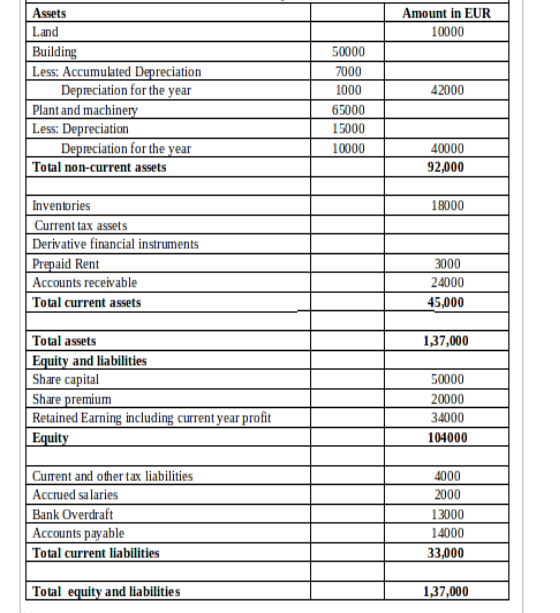
(c) Accounts Concepts: Consistency and Prudence:
Accounting concepts include fundamental assumptions, rules, and principles that provide a basis for the recording of accounting transactions and the preparation of final accounts. Accounting is purely based on principles and accounting principles are framed based on some assumptions; such assumptions are also known as accounting concepts (Bushman and Smith, 2001).
Consistency: As per this accounting concept, accounting policies adopted by business organizations should be applied consistently from one period to another. Change in adopted accounting policies and assumptions is allowed only in case it is required by relevant statute or change would result in a better presentation of accounts.
Prudence: As per this accounting concept, business organizations should record expenditures and obligations or liabilities as soon as they occur, whereas revenues and incomes should be recorded when realized.
(d) Purpose of Depreciation in Formulating Accounting Statements and Methods of Depreciation:
Depreciation is provided to show the decrease in assets arises due to physical wear and tear and obsolescence of assets during a particular period (Holthausen and Watts, 2001). Depreciation simply exhibits the real consumption of a particular asset. The following are major methods to calculate depreciation:
Straight-line method: Under the straight-line method, an equal amount of depreciation is provided during the whole useful life of the asset. This is a simple and widely used method of depreciation. The formula of depreciation under this method is:
Cost of assets less Residual value
Total Useful life of the asset
Written-down value method: Under this method, a certain formula is used to calculate a fixed percentage of depreciation, and such percentage is applied to the book value of the asset to get the amount of depreciation for the year. This method is used for assets that have more efficiency in the beginning and thereafter decrease year after year (Libby, Bloomfield, and Nelson, 2002). This method is usually adopted for plant and machinery, fixtures and fittings, motor vehicles, etc.. This is the formula for the calculation of the rate of depreciation:

Stuck with your Assignment?
Hire our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS and Get 100% Original Document on any Topic to Secure A+ Grade
Get Assignment Help
CLIENT 4
Purpose of bank reconciliation: A bank reconciliation statement is prepared by the organization to reconcile the amount of the bank account prepared by the organization with the amount shown in the bank statement or passbook of the bank (Edwards, 2013).
Reason for variation in the cash book and bank statement: Due to the deposit of any amount by customers directly into a bank account, bank charges charged by the bank and organization unaware of the fact, checks issued but not presented, etc. are major reasons for the difference in the balance of cash book and bank statement as on a particular date (Bank reconciliation statement, 2017).
(i) Bank Reconciliation Statement on 1st December 2017:
Its purpose is to reconcile the balance of the bank of books of accounts with the passbook.
|
Bank reconciliation statement on 1st December 2017 |
|
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Bank Balance as per passbook |
17478 |
|
Less: Suspense due to wrong carry forward |
987 |
|
Actual balance as per cash book after reconciliation |
16491 |
(ii) Durrell Ltd's Updated Cash Book for December 2017 :
|
Updated Cash Book for December Month |
|||||
|
Particulars |
|
Amount |
Particulars |
|
Amount |
|
Balance B/d |
|
16491 |
Alexander |
|
857 |
|
Suspense A/c |
|
987 |
Bank Charges |
|
47 |
|
Able |
|
962 |
Burgess |
|
221 |
|
Baker |
|
1103 |
Barry |
|
511 |
|
Direct deposit by customer |
|
176 |
Cook |
|
97 |
|
Charlie |
|
2312 |
Payment |
|
120 |
|
Delta |
|
419 |
Hay |
|
343 |
|
Instrument No. 785 |
|
106 |
Rent |
|
260 |
|
Echo |
|
327 |
Instrument No. 780 |
|
426 |
|
Cash Sales |
|
529 |
Instrument No. 781 |
|
737 |
|
Fred |
|
119 |
Instrument No. 310923 |
|
297 |
|
Instrument No. 787 |
|
260 |
Standing order rates |
|
137 |
|
|
|
|
Balance c/f |
|
19738 |
|
Total |
|
23791 |
Total |
|
23791 |
(iii) Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st December 2017:
|
Bank Reconciliation Statement |
|||
|
Particulars |
|
|
Amount |
|
Bank Balance as per passbook |
|
|
19738 |
|
Add: Items having effects of higher balance in the cash book. |
|
|
|
|
The cheque was deposited but not yet cleared. |
|
120 |
|
|
Bank charges are not recorded in the cash book. |
|
47 |
|
|
Payment by the bank is not recorded in the cash book. |
|
|
|
|
|
Instrument No.780 |
|
426 |
|
|
Instrument No.781 |
|
737 |
|
|
Instrument No.310923 |
|
297 |
|
Adjustment for standing order rates |
|
137 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Items having effects of lower balance in cash book |
|
||
|
Check issued but not yet presented for payment. |
|
|
|
|
|
Instrument No. 785 |
106 |
|
|
|
Instrument No.787 |
260 |
366 |
|
Direct deposit by customer |
|
176 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank balance as per cash book (Should be) |
20960 |
||
|
Less: Opening Balance difference (17478-16491) |
987 |
||
|
Actual balance as per cash book after reconciliation |
19973 |
||
CLIENT 5
In the books of Henderson for January 2018
(a) Sales Ledger Control and Purchase Ledger Control Account:
- i) Purchase Ledger Control A/c
|
Purchase Ledger Control A/c |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount (£) |
Particulars |
Amount (£) |
|
Discount Received |
550 |
Balance b/d |
10160 |
|
Purchase Return |
2110 |
Credit Purchase |
106500 |
|
Bank/Cash (Payment to suppliers) |
111010 |
Bank/Cash (Refund from supplier) |
400 |
|
Set-off (Transfer from sales ledger) |
540 |
|
|
|
Balance c/d |
2850 |
|
|
|
Total |
117060 |
Total |
117060 |
|
|
|
Balance b/d |
2850 |
(ii) Sales Ledger Control A/c
|
Sales Ledger Control A/c |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount (£) |
Particulars |
Amount (£) |
|
Balance b/d |
9600 |
Sales Return |
5320 |
|
Credit Sales |
142350 |
Bad Debts |
1200 |
|
|
|
Discount Allowed |
960 |
|
|
|
Bank/Cash (Receipt from credit customers) |
150610 |
|
Balance c/d |
6680 |
Set-off (Transfer to purchase ledger) |
540 |
|
Total |
158630 |
Total |
158630 |
|
|
|
Balance b/d |
6680 |
(b) Control Account:
A control account refers to a general ledger account that shows only the total amount of different ledgers like a summary (Khan and Mayes, 2009). The amount of each control account is also found in the subsidiary ledger. Balance of control accounts shows the sum of the balance of all accounts. The situations that attract the need to prepare a control account in the context of Henderson are as follows:
- A control account is required to show a managed summary of different ledgers and accounts.
- A control account is a tool used by accountants to reconcile costs and final accounts.
- Control account assists in the preparation of profit and loss and financial statements quickly and in an easy manner (Saunders, Cornett, and McGraw, 2006).
- Control accounts are prepared by accounts as an activity of internal checks or account balances and transactions.
CLIENT 6
(a) Suspense Account:
A suspense account is a temporary general ledger account prepared for the posting of uncertain entries and irregularities pending and unclassified amounts. Practically amounts, transactions, or balances that are unidentified before the finalization of the account are recorded in a suspense account until these amounts are allocated (White, Sondh, and Fried, 2005).
Main features of the suspense account:
- Suspense accounts help to match the trial balances on a temporary or permanent basis.
- These accounts assist in the quick Identification of errors by showing mismatched amounts in trial balance (Baldwin, Ingram, and Albright, 2007).
- Suspense account presents possible misstatements in the final account and assist in the identification of the source of the misstatement.
- It is very easy to allocate one-sided errors by using a suspense account and it also helps to evaluate errors.
(b) Preparation of Trail Balance:
|
Ledgers |
Debit |
Credit |
|
Purchase Account |
700 |
|
|
Sales Account |
|
1100 |
|
Rent Paid |
250 |
|
|
Cash in bank |
840 |
|
|
Travel expense |
160 |
|
|
Receivables |
320 |
|
|
Payables |
|
350 |
|
Opening Inventory |
220 |
|
|
Capital Account |
|
710 |
|
Control Account |
|
330 |
|
Total of all balances |
2490 |
2490 |
(c) Journal Entries to Show Necessary Corrections for Eliminating Suspense Account Balance:
Journal Entries
|
Particulars |
Debit |
Credit |
|
Simon A/c To Smith A/c (The sale was debited to Smith instead of Simon.) |
220 |
220 |
|
Jones A/c Dr To Suspense A/c (The sale of £420 now entered in JoJones's account, now entered.) |
420 |
420 |
|
Suspense A/c Dr To White A/c (being the purchase of £750 not entered in the White account, now entered) |
750 |
750 |
Dr. Suspense Account Cr.
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
|
To White A/c |
750 |
By opening balance |
330 |
|
|
|
By Jones A/c |
420 |
|
Total |
750 |
Total |
750 |
(d) Difference Between a Suspense A/c and Clearing A/c:
Suspense accounts are mainly prepared by an accountant of a business firm in case of any error or omission found within the account. In case the balance of the trial balance on the credit and debit side shows a different balance, the accountant should use it to open a suspense account until the problem is identified. On the other side, clearing accounts are mainly prepared by the bookkeeper of an organization that helps them to record financial dealings temporarily. They wait for a suitable time and post the transaction into a permanent account. Clearing accounts can also be used in a way for accounts receivable (Peterson, 2005).
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, it has been stated that accounting practices are being implemented by accountants of companies to maintain records, reports, and financial statements at the end of an accounting year. Generally accepted accounting standards are followed by the accountant of the company so that statements are reliable and free from any type of error. Management of an organization makes sure that to increase the reliability and credibility of fiscal statements there must be proper use of accounting standards. Reporting under the financial accounting process builds the trust of users of financial statements in business organizations, which creates potential long- or short-term advantages for business organizations.
REFERENCES
- Edwards, J. R., 2013. A History of Financial Accounting (RLE Accounting). Routledge.
- Fourie, M. L., and et. al., 2015. Municipal finance and accounting. Van Schaik Publishers.
- Hale, T. N., Hale, T., and Held, D. eds., 2012. Handbook of transnational governance. Polity.
- Hall, J. A., 2012. Accounting information systems. Cengage Learning.
- Jönsson, S., 2013. Accounting and business economics traditions in Sweden: A pragmatic view. In Accounting and Business Economics (pp. 203-219). Routledge.
- Mullinova, S., 2016. Use of the principles of IFRS (IAS) 39, "Financial instruments: recognition and assessment," for bank financial accounting. Modern European Researches. (1). pp. 60-64.
- Bushman, R.M., and Smith, A.J., 2001. Financial accounting information and corporate governance. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 32(1-3). pp. 237-333.
- Holthausen, R.W., and Watts, R.L., 2001. The relevance of the value-relevance literature for financial accounting standard setting. Journal of accounting and economics. 31(1-3). pp. 3-75.
- Libby, R., Bloomfield, R., and Nelson, M.W., 2002. Experimental research in financial accounting. Accounting, Organizations, and Society. 27(8). pp. 775-510.



 Company
Company


















