SECTION A - CRITICAL ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
Task 1: Big Data Principles in the Cloud
Introduction
The retail industry is experiencing a radical change of its nature brought about by the incorporation of digital technologies as one of the prominent accelerators of operational intelligence, whereby Big Data plays a pivotal role in this context. In the case of companies such as Green Basket (GB) which is an expanding UK based chain of supermarkets, collecting, processing and responding to large volumes of information over long distances has become a necessity (Sandhu, 2022). Nowadays data and information technologically advanced world is extremely competitive, and the strategic importance of Big Data is also based on the speed with which the amount of information collected can be processed into action-oriented information.
Big Data Characteristics
The five most widely used definitions of Big Data consist of the five main features that have been used to characterize the concept of big data; Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity and Value as a mechanism of depicting the complexity and potential that big data environments possess:
- Volume: GB has 14 physical stores, online shops and central databases. This incorporates sales records, customer information, records of inventory, and delivery information which keep adding at a blistering rate(Syed Thouheed Ahmed et al., 2021). The magnitude itself renders the business of traditional data handling to be inefficient.
- Velocity: The old systems used in the company process data at night, something that prevents the generation of timely insights. High data velocity is needed in retail where pricing, stock quantity and customer preference are changing every hour(Mishra et al., 2022). Real time analytics may assist in dynamic pricing and restocking of inventory proactively.
- Variety: GB data covers both structured format (e.g., POS records, CRM records), semi-structured format (e.g., data in the form of a web log), and unstructured format (e.g., customer feedback, email). These various sources can be brought together by cloud-based Big Data platforms to analyze them extensively.
- Veracity: A few customer complaints are based on failure to fulfil the orders as indicated by low reliability of data. Duplication of records, unverified information or missing details are crippling business decisions. A Big Data strategy improves the quality of the data by means of validation and cleansing pipelines.
- Value: The eventual point of Big Data is to create valuable business. Understanding customer behaviour, sales patterns and stock assignment will also enable GB to make better product placement and to optimize the logistics and even increase customer engagement.
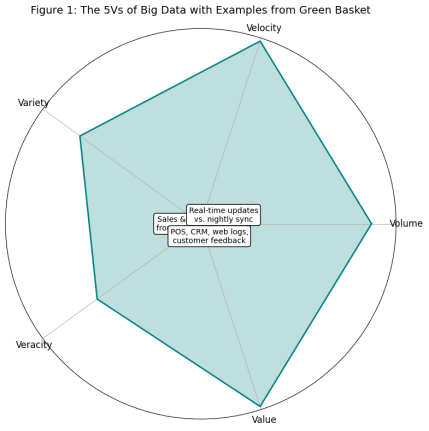
Figure 1: Big Data Principles in the Cloud
Role of Cloud in Big Data
The implementation and scalability of the Big Data systems have been redefined by cloud computing. Its elasticity enables the businesses to increase or decrease storage and computing capacities on-demand and distributed architectures provide high availability and fault resistance (Bajaj, Sharma and Singh, 2021). In the case of GB that needs to serve several data streams across various stores that are located in different geographical regions, a centralized cloud will eliminate the constraints posed by local infrastructure.
In addition, the cloud facilitates real-time data analytics with an integrated and stream processing, data warehousing, and AI/ML tools (Dalal, 2025). Cloud providers, such as Azure, AWS or Google Cloud provide native source Big Data services which ingest, transform and visualize least expected manual settings.
Cloud also has the power to provide access and centralized control worldwide, which allows stakeholders at different levels to store managers, regional analysts, or executives to have safe access to real-time consistent information (Arif and None Subhi R. M. Zeebaree, 2024). This breaks the latency of the manual report exchange and improves decision-making cooperation.

Benefits for Green Basket
A cloud-based Big Data solution could provide Green basket with a number of real opportunities:
- Real-Time Synchronization: The most tangible benefit of this is the substitution of overnight data updates with real time data synchronization. This helps in proactive control particularly on high demand or perishable stock.
- Improved Decision-Making: Store managers will also have real-time dashboards, and they will monitor sales, stocks, and customer preferences upon demand. This expedites the strategic changes and increases responsiveness to the local market needs.
- Better Customer Satisfaction: Real Time customer order tracking and precise stock visibility will alleviate delays and stock outs which stick versions of the customer concerns and enhance shopping.
- Operational Efficiency: Speed and efficiency of the data flows decrease human error, liberate staff to provide services to customers, and enhance overall delivery of services.
These advantages are in line with the strategic goals of GB to increase performance and maintain leadership in the organic grocery division.
Hurdles and Factors.
Although having benefits, the cloud-based big data paradigm can also lead to some challenges:
- Data Security and Privacy: Any time GB transition data containing sensitive information about customers and operations to cloud computing, it has to mitigate the risk of unauthorized users and data breaches as well as regulatory compliance. It will require strong encryption and access control and auditing.
- Vendor Lock-In: Selecting one cloud vendor could be an impediment to flexibility(Weldemicheal, 2023). GB needs to make its cloud architecture in such a way that it is modular and interoperable so as not to be entangled with a single ecosystem.
- Cost Management: Although cloud implementation saves on start up capital expenditure operational costs may increase with the size of the data to be stored and the amount of compute. There are obligatory cost governance structures and auto-scaling policies.
- Data Governance: Data Governance policies are needed to ascertain consistency, accuracy and compliance in case of decentralized data entries.
Such aspects need to be planned in advance and handled by collaborating with reputated cloud security vendors (Harauzek, 2022).
Get support from an expert assignment helper.
Task 2: Security Risks in IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Models
History of Cloud Service Models.
Cloud computing has been designed based on three foundational service models such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service(PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), which provide a different level of control, capacity to vary, and shared responsibility (Fatima, Sumra and Naveed, 2024).
The IaaS offers the user with virtual computers resources on the internet. It is a case of users taking control of the operating system, storage, applications, and data, whereas the physical infrastructure is managed by the cloud provider. Examples are Amazon EC2 and Microsoft Azure Virtual machines (Sharifzadeha, Malekpoura and Shojab, 2022).
PaaS provides an application development platform that requires minimal maintenance due to a range of features such as management and hardware-free application construction, meaning users handle applications only. Such services as Azure App Services and Google App Engine provide an environment, run-times, development tools and databases.
Relevant SaaS involves web-based software applications that are fully managed. The provider manages the entire stack, comprising infrastructure, platform and application management. They are Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365.
All these models depict different degrees of abstraction and responsibility, both of which determine the security risks organisations should take into consideration and address.
Each Model Security Risks.
The IaaS is the most flexible but also presents the utmost responsibility regarding the security management.
All sorts of misconfigurations on the virtual networks, storage permissions or firewall rules are typically common which may open sensitive data to unauthorized access.
Hypervisor attacks adopt the vulnerabilities in the virtualization layer that may enable the attackers to leave one virtual machine and enter others within the same host environment.
There is always a threat of being caught by the known exploits when the user does not update software and systems on a regular basis, hence exposing them to unpatched systems.
PaaS eliminates infrastructure management overheads but has its own challenges.
- The vulnerability of APIs is also a particular concern because vulnerable or poorly secured APIs can be used as the vectors of attacks(Yu, 2021). At the same time, APIs can reveal essential business functions without an appropriate confirmation and encryption.
- Minimal access to underlying systems can make organizations not to tailor security made available like deep packet inspection or intrusion prevention systems.
- Shared responsibility confusion may arise when the developers have wrong assumptions of the provider being in-charge of all the security measures, hence neglected the applications level security.
- SaaS is also much easier to use at the expense of visibility and control.
- When the customer information is on the infrastructure of the vendor, there will be data governance issues. Companies have to leave the task of data security and regulatory issues to the provider(Singh et al., 2025).
- Security managed by a vendor might not be consistent with the internal security policy or the risk tolerance of a company. An attack on vendor level may violate customer information.
- Absence of security setting customization hinders the right to apply an access control fine-tuning or use it with internal identity management systems.
Suitability is appropriately named.
The infrastructure used in Green Basket is now decentralized and data is synchronized once every day and they have manualized processes as well as poor security measures. The company needs a solution which will beenabled in real-time, provide strong security and the ability to scale without the physical or virtual infrastructure overhead.
Although IaaS is flexible, there is a high rate of internal technical expertise that would be required to handle the operating systems, security patches and network configuration, which GB might lack.
SaaS is not customizable or integrates well to achieve what Green basket requires to engaging in real-time analytics, custom dashboards, system-wide integration, etc. SaaS is easy to implement; however, it lacks the flexibility and ability to meet the needs of a company seeking real-time analytics, custom dashboards, and system-wide integration.
PaaS presents the best of both worlds whereby applications/data level control is available yet the infrastructure and system management are off-loaded to the service provider. This facilitates a scaled expansion, uninterrupted continuity with analytics providers, and better security positioning.
Justification of Selecting PaaS.
Implementation of PaaS will enable Green Basket to dwell on innovations and analytics and enjoy secure and highly scaled infrastructure that is managed by the professionals.
Access to application logic, databases and data flows are used to build control and usability whereas the background operations (scaling and patching) are automated.
PaaS vendors such as Microsoft Azure offer security solutions such as advanced identity management and encryption systems, as well as compliance standards, aimed at global standards.
Scalability is also implemented through automatic booking of resources so that there is a constant performance when there is high demand.
Analytics solutions like Power BI and Azure Synapse can be integrated to facilitate centralized monitoring and live decision making of all the stores in the 14 locations(Ojo and covey, 2025).
Fast cycles of development are made possible by pre-configured environments so that developers can roll out new features or fixes efficiently and within a short period of time and therefore reduce downtime and agility increases.
This model serves the strategic objectives of GB of being digital modernized, efficient in operations, and groundbreaking in customer service.
See this assignment example for better understanding.
Risk Mitigation Strategies.
In order to have security in a PaaS set up, Green Basket must have in place controls of industry standards:
- Role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) is the Identity and Access Management (IAM) that provides access to sensitive resources to only the authorized individuals.
- At rest and during transit, data should be encrypted, and key management should be done safely by using such type of services like Azure key vault or AWS KMS.
- The use of firewall and network security settings should restrict the exposure of the public to private endpoints and restricted access policy.
- Threat detection and monitoring tools such as Azure Security Center, AWS GuardDuty or Google Cloud SCC are tools that offer real-time warnings and information about suspicious activities.
- Transparency and accountability are assured because of audit logging and compliance tracking. There is also log immutability which facilitates regulatory audits and internal audit reviews.
With these strategies in place, Green Basket will be able to confidently use cloud without having to face too many vulnerabilities and losses of customer confidence.
Task 3: Big Data Frameworks and Security Countermeasures
Internal Big Data in the Cloud Frameworks.
With businesses moving on to cloud-based infrastructures, it becomes crucial to determine the right type of Big Data framework to ensure seamless data integration and analytics and security. A number of frameworks have become industry-standards especially when implementing cloud-native environments.
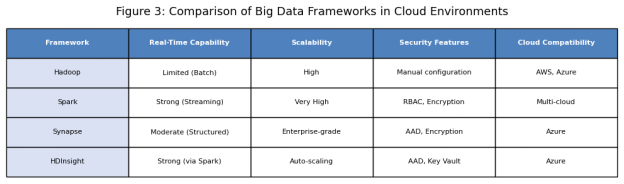
Apache Hadoop is a developed system of distributed data storage and batch processing. Although it can be highly relied on to undertake large-scale, offline analytics, its design is not created to undertake real-time operation hence is not best suited in use cases that need immediate insights(Heuchert et al., 2021).
Apache Spark builds on the feature of Hadoop by providing the in-memory features of data processing, which are much faster and more efficient. It is also highly versatile in business intelligence tasks as it supports real-time processing as well as batch and stream processing.
Azure HDInsight is a cloud-based service provider of Microsoft, which is compatible with various Big Data systems, such as Spark and Hadoop. It is simple to deploy, scale and secure on a cloud-native (Harauzek, 2022).
Azure Synapse analytics combines both data warehousing and big data analytics. It is scaled to analytics on an enterprise level but can be more applicable to organizations that have advanced analytics needs as well as have large volumes of structured data.
Considering the priorities of the operation, presented by Green Basket, namely, real-time decision-making, cost-efficiency, and smooth integrability, the Apache Spark, which is implemented using a platform of Azure HDInsight, is the most appropriate option.
Framework Selected Apostle Spark on Azure HD Insight
One of the boundaries that Apache Spark has earned the greatest repute is the real-time processing of data though it enables organizations to take immediate action to business-sensitive events. Spark also greatly enables the reduction in the latency of the conventional batch processing, as provided by in-memory computing, and is thus best suited to support dynamic inventory updates, fraud detection, and live customer order tracking, all of which are essential to the transformation of GB.
Azure HDInsight provides the ability to deploy Spark clusters with great ease to benefit of the minimal overhead. Being a fully managed service, it is highly available in autoscaling and is also easy to combine with other Microsoft services such as Azure Data Lake storage, Power BI and Azure machine learning (Singh et al., 2025).
This mix is capable of enabling Green Basket to:
- Actually this keeps absorbing and processing data around 14 retail locations.
- Produce real-time information to the store managers.
- Construct safe pipelines on request to customers and update of stock and tracking of deliveries.
The inherent support with Power BI also enables business people, as it allows transforming complex datasets into interactive dashboard without any specific technical expertise.
Security Features
The security is a basic need of Green Basket based on the recent happening with the database outages and security breaches. Apache Spark on Azure HDInsight offers the following strengths to function as a secure system to handle them:
- In-built Authentication and Authorization: Azure Active Directory (AAD) Integration with Azure Active Directory (AD) provides user authentication of single sign-on and role-based access control (RBAC). This restricts access control on the user roles and responsibilities.
- Encryption at Rest and In Transit: Sensitive data is never accessed by unauthorized individuals as TLS encrypts data during transmission and leaves it stored using Microsoft managed keys or customer managed keys in Azure Key Vault.
- Azure Key Vault: It is a service used to store secrets, including API keys, certificates and passwords, in a centralized and highly secure place. It also can integrate with Spark jobs as credentials are not hard-coded or on display.
- Private Networks and Firewalls: HDInsight clusters could be isolated with the help of virtual networks (VNets) and restrict the access to only a specific range of IPs(Trisolino, 2023). This plays a great role in minimizing external threats.
- Monitoring and Threat Detection: Azure incorporates Sentinel, Monitor, and Log Analytics to monitor unusual activity, identify and produce real-time alerts, and threats. This enhances the response time and visibility of operations.
Speaking of the Specific Concerns of GB.
The necessity behind the digital overhaul of Green Basket consists of eliminating any outages, protecting data integrity, and increasing access speed. Apache Spark on HDInsight is a direct result of the following priorities:
- Processing outages: Outages Up to 98 percent of the Risk: HDInsight is high-availability and the cluster heals by itself. In addition, Spark jobs are also resistant and may resume on a failover of a node without re-initiating the whole pipeline.
- Prevention of Data Breaches: The weak protocols in the existing system of GB resulted in security breaches. These vulnerabilities are closed with HDInsight using RBAC, encrypted communications, and central secret administration(L'Esteve, 2022).
- Enhancing Data Reliability and Access: Real-time processing means that the data is always up to date, and the information is relevant to the current situation in the stores. This puts away delays associated with the synchronization at the end of the night, as well as manual sharing of reports.
Task 4: Infrastructure Diagram and Explanation
Cloud Infrastructure A. Overview.
The suggested cloud infrastructure will provide the real time flow of the data of all 14 stores of Green Basket into a centralized environment launched in Microsoft Azure (Ganesh and Rao, 2025). All the stores deliver transaction information, inventory, and interactions with customers to a secure cloud system to make unified analytics and decisions.
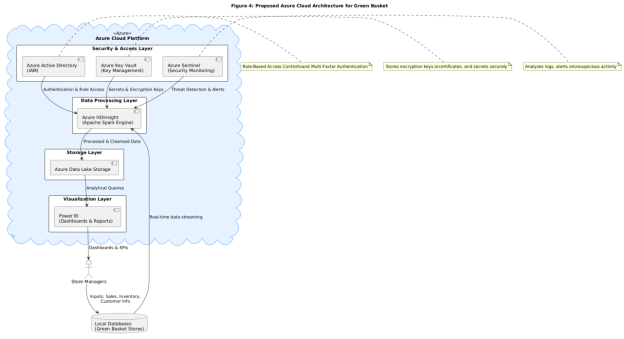
Figure 3: Proposed Azure Cloud Architecture
Tools Included
The major elements featured in it are Azure HDInsight (including Apache Spark) to process data, Azure Data Lake Storage to keep data in a scalable manner, Power BI to create real-time dashboards, and Azure Sentiment to monitor threats. Strict data protection and access are enabled by IAM through the Azure Active Directory, Azure Key Vault, and private networks.
SECTION B - IMPLEMENTATION
Introduction
This part illustrates the way in which the proposed cloud based Big Data solution can be implemented practically in the case of Green Basket. It will convert the architectural and security choices outlined in Section A into a practical situation, revolving around the mechanisms of data migration, processing, securing and visualising in a cloud context (Azam et al., 2023). The focus is made on the end-to-end data flow, including the store-level data ingestion to the centralised analytics and management reporting. A scaffold proof-of-concept cloud application will be used to back this implementation to show the viability and success of the chosen Platform as a Service (PaaS) model and cloud-based analytics solution.
Read more sample : Barriers to Implementing the Circular Economy: Challenges and Managerial Solutions
Task 1: Big Data Project Implementation in the Cloud
Existing System Overview
Green Basket has a decentralised data structure, whereby every store has local database where sales, inventory, and daily transactions are maintained. Simultaneously, a web sales system produces more customer order and delivery information. Information between stores and the central system is timely synchronised overnight and store managers use manually shared reports to make decisions (Venkataarangam, 2025). Such a solution results in slow insights, a lack of real-time visibility, and system downtime as a regular occurrence in the process of backup and synchronisation.
Data Selected for Migration
Its implementation aims at migrating the key operational datasets which are critical towards real-time analytics and management oversight. These are sales transactions, stock quantities, order records of customers and store identifiers and related timestamps. These data sets have been chosen since they have a direct impact on stock management, order fulfilment and sales performance which were found to be key areas of concern in the Green Basket situation.
Cloud Environment and Service Model
The Platform as a Service (PaaS) model was chosen with the use of Microsoft Azure, which corresponds to the analysis in Section A as it allows controlling the application level and settles the burden of infrastructure maintenance, patches, and scalability to the cloud system (Mathur, 2024). Azure has been selected because it is scalable, has lesser operation overheads, and comes with inbuilt security features, which is appropriate to an organisation with limited in-house cloud expertise.
Implementation Approach
The first type is an initial batch migration, which will move historical data into the cloud environment and the second type is the continuous ingestion of new transactional data to recreate near real-time updates. A python-based cloud-based application is used to store and process data centrally to conduct aggregation, clean, and analyze it (Kabir et al., 2024). This method is lightweight, but it mimics the Big Data processing, as it can process several data sources and produces consolidated information at scale.
Figure 4: Deployment of Python project in Azure
Advantages realized by Green Basket
The implementation gives real-time access to sales and inventory information and this has greatly minimized the data latency. It will improve the store managers and executives in making decisions and will provide a platform of scalability in future Big Data and advanced analytics programs.
Task 2: Security Controls Demonstrated in the Big Data Project
Security Risks Identified
Migration to a cloud-based Big Data environment poses a number of threats, such as the unauthorised access to sensitive data, the interception of transmitted data, the possible loss of data or the unavailability of the services, and poor governance in the case of undefined cloud responsibilities (Gopalakrishna Karamchandz, 2025).
Identity and Access Management
Role-based access principles are used conceptually to control the access to the cloud application. Various user roles are supposed to be assigned different access privileges, e.g. the management and the operational staff assume two different user roles, as only authorised personnel would get sensitive insights to the business.
Data Protection Mechanisms
The information sent between the users and the cloud application is secured with the help of HTTPS that guarantees the encryption of data sent over the air (Seth et al., 2020). The data is safely processed in the application, and no credentials are embedded in the source code and thus there is less risk of exposing credentials.
Platform and Network Security
Its implementation is based on applications that are security enforced by cloud platform such as application hosting that is secured and limited endpoint exposure. Such controls lower the attack surface and take advantage of the infrastructure-level protection of the cloud provider.
Surveillance and Accessibility
Cloud hosting gives the application 24/7 availability, whereas simple logging and monitoring services allow the system to be reliable (Gireesh Kambala, 2023). All these actions will help to ensure that the data of Green Basket is kept confidential, intact, and available (CIA).
Task 3: Design of a Data-Driven Management Dashboard
Purpose of the Dashboard
The dashboard will facilitate operational and strategic decision-making as it will be used to substitute manual reporting with real-time and data-driven insights. It increases visibility of management in all Green Basket stores.
Dashboard Technology Choice.
The cloud-based web dashboard is executed with the help of a Python analytics layer, and a web interface to make it accessible (Gupta and Sharma, 2023). The method provides the management with the chance to get the results of the insights at any place and without the need to use any special software.
Key Metrics Displayed
The dashboard indicates total revenue, total quantity sold, number of active stores, revenue by store, daily revenue trend, and identification of the high selling products. These indicators are an all-encompassing business performance overview.
Interactive Features
Such interactive capabilities as store-level filtering and dynamic updates enable users to browse data on various levels of detail. Visual graphs assist in the analysis of the trend and enhance the interpretability of the performance data.
Value to Green Basket Management.
Dashboard allows the quicker recognition of the performance problems, inventory and sales planning, and better monitoring of the business activities as well as the system performance (Akter and Kudapa, 2024).
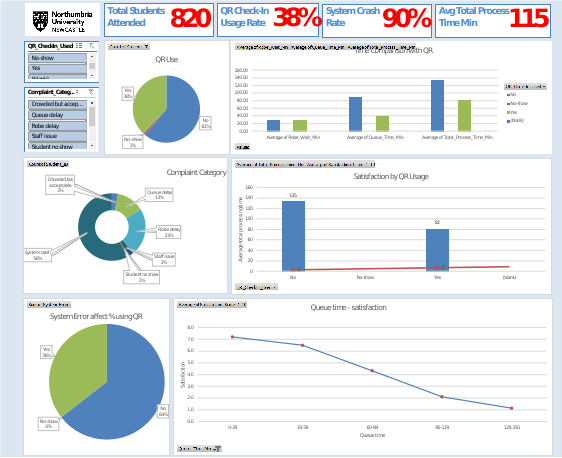
Figure 5: Dashboard
Task 4: Professional, Legal, Ethical, and Social Practices
The effect is that the implementation is aligned with the UK GDPR requirements as it ensures that the customer and transactional data is processed legally, in accordance with the data minimisation principles, and the use of the data is restricted to the specific business purposes. Responsible use of information, transparency, and preventive misuse are some of the ethical aspects that promote ethical data usage. Professional practices involve the ability to design secure systems, review access control on regular basis, and staff understanding of their roles in data protection (Sargiotis, 2024). Socially, a better service reliability and less customer complaints contribute to the level of trust and prove to the customers that Green Basket is serious about the security and efficiency of its digital operations.
Conclusion
As a conclusion, this part has shown that a secure cloud-based solution to Big Data application in Green Basket can be practically implemented. The proof-of-concept cloud application, which is lightweight, has been applied to demonstrate the viability of migrating operational data, implementing security controls and providing real-time management dashboards. The implementation is emphasized on the manner in which the cloud-based analytics could help reduce the data latency, enhance the system availability, and provide a better view across several stores. Taken together, the above results will facilitate better decision-making, better operational performance, and compliance with the strategic purpose of Green Basket, which is to become digitally transformed with the help of secure and scalable cloud solutions.
REFERENCES
- Akter, M. and Kudapa, S.P. (2024). A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE-INTEGRATED BI DASHBOARDS FOR REAL-TIME DECISION SUPPORT IN OPERATIONS. International Journal of Scientific Interdisciplinary Research, 05(02), pp.158-191. doi:https://doi.org/10.63125/47jjv310.
- Arif, N.Z. and None Subhi R. M. Zeebaree (2024). Distributed Systems for Data-Intensive Computing in Cloud Environments: A Review of Big Data Analytics and Data Management. Indonesian Journal of Computer Science, 13(2). doi:https://doi.org/10.33022/ijcs.v13i2.3819.
- Azam, M., Nasim, F., Ahmad, J. and Bhatti, S.M. (2023). A Security Framework for Data Migration over the Cloud. Journal of Computing & Biomedical Informatics, [online] 7(02). Available at: https://www.jcbi.org/index.php/Main/article/view/602.
- Bajaj, K., Sharma, B. and Singh, R. (2021). Implementation analysis of IoT-based offloading frameworks on cloud/edge computing for sensor generated big data. Complex & Intelligent Systems. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-021-00434-6.
- Dalal, A. (2025). Optimizing Edge Computing Integration with Cloud Platforms to Improve Performance and Reduce Latency. SSRN Electronic Journal. doi:https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5268128.
- Fatima, E., Sumra, I.A. and Naveed, R. (2024). A Comprehensive Survey on Security Threats and Challenges in Cloud Computing Models (SaaS, PaaS and IaaS). Journal of Computing & Biomedical Informatics, [online] 7(01), pp.537-544. Available at: https://jcbi.org/index.php/Main/article/view/403.
- Ganesh, N. and Rao, T.S. (2025). Advancing Sustainability in Cloud Computing: Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation and Green Infrastructure Strategies. doi:https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5138669.
- Gireesh Kambala (2023). Designing resilient enterprise applications in the cloud: Strategies and best practices. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 17(3), pp.1078-1094. doi:https://doi.org/10.30574/wjarr.2023.17.3.0303.
- Gopalakrishna Karamchandz (2025). Secure and Privacy-Preserving Data Migration Techniques in Cloud Ecosystems. Journal of Data Analysis and Critical Management, [online] 1(02), pp.67-78. Available at: https://jdacm.com/index.php/jdacm/article/view/36.
- Gupta, U. and Sharma, R. (2023). A Study of Cloud-Based Solution for Data Analytics. Internet of things, [online] pp.145-161. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-33808-3_9.
- Harauzek, D. (2022). Cloud Computing : Challenges of cloud computing from business users perspective - vendor lock-in. [online] www.diva-portal.org. Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:1679817.
- Heuchert, S., Bhaskar Prasad Rimal, Reisslein, M. and Wang, Y. (2021). Design of a small-scale and failure-resistant IaaS cloud using OpenStack. doi:https://doi.org/10.1108/aci-04-2021-0094.
- Kabir, M.A., Ahmed, F., Islam, M.M. and Ahmed, Md.R. (2024). Python For Data Analytics: A Systematic Literature Review Of Tools, Techniques, And Applications. ACADEMIC JOURNAL ON SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, ENGINEERING & MATHEMATICS EDUCATION, [online] 4(04), pp.134-154. doi:https://doi.org/10.69593/ajsteme.v4i04.146.
- L'Esteve, R. (2022). The Azure Data Lakehouse Toolkit. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-8233-5.
- Mathur, P. (2024). Cloud Computing Infrastructure, Platforms, and Software for Scientific Research. Series in bioengineering, [online] pp.89-127. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1017-1_4.
- Mishra, K., Bhattacharjee, V., Saket, S. and Mishra, S.P. (2022). Cloud and Big Data Security System's Review Principles: A Decisive Investigation. Wireless Personal Communications, 126(2), pp.1013-1050. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09781-0.
- Ojo, S. and covey, A. (2025). Identity and Access Management (IAM) Authentication Methods: Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) and Access Control Models. [online] doi:https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202503.1830.v1.
- Sandhu, A.K. (2022). Big data with cloud computing: Discussions and challenges. Big Data Mining and Analytics, [online] 5(1), pp.32-40. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9663258/.
- Sargiotis, D. (2024). Data Security and Privacy: Protecting Sensitive Information. Data Governance, [online] pp.217-245. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67268-2_6.
- Seth, B., Dalal, S., Jaglan, V., Le, D., Mohan, S. and Srivastava, G. (2020). Integrating encryption techniques for secure data storage in the cloud. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 33(4). doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.4108.
- Sharifzadeha, M., Malekpoura, H. and Shojab, E. (2022). Cloud Computing and Its Impact on Industry 4.0. Industry 4.0 Vision for Energy and Materials, pp.99-120. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119695868.ch4.
- Singh, S., Alam, M.N., Kaur, B., Kaur, K., Kaur, S. and Hossain, S. (2025). Comparative analysis of Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark for business intelligence. AIP conference proceedings, [online] 3224, pp.020040-020040. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0246086.
- Syed Thouheed Ahmed, Syed Muzamil Basha, Sajeev Ram Arumugam and Kiran Kumari Patil (2021). Big Data Analytics and Cloud Computing. MileStone Research Publications.
- Trisolino, A. (2023). Analysis of Security Configuration for IDS/IPS. [online] webthesis.biblio.polito.it. Available at: https://webthesis.biblio.polito.it/29003/.



 Company
Company


















