Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a popular programming paradigm, which builds software design based on objects that model real-world objects and their interrelations. OOP allows the building of modular, reusable and maintainable systems through the combination of data and behaviour in classes, which make it appropriate with large and complex applications (Hasan, 2025). OOP has four fundamental concepts, including encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance and polymorphism, which facilitate data security, lower complexity, encourage reuse of code, and increase flexibility of the system. OOP is especially useful to the health care systems, where patients, doctors, appointments, schedules, etc. can be intuitively modelled to enhance clarity in the systems, minimize errors, and provide dependable and scalable solutions to handling appointments in hospitals.
Introduction to the Hospital Appointment Management System (HAMS)
This is due to the fact that healthcare organisations usually use manual or semi-digital systems in order to manage patient appointments, which may cause inefficiencies, scheduling problems, and administrative overload. The problems that are common are the duplication of appointments, lack of the visibility of the schedule of doctors, and the lack of the clearly defined roles of users. These difficulties may have an impact on the efficiency of work and patient experience, especially in busy-clinical settings where accurate information and the accessibility of the information in a timely manner is vital.
Hospital Appointment Management System (HAMS) emerges as a solution to these issues in an organized and object-oriented way. The system will be structured upon three key actors, including Patients, Doctors, and Administrators. The patients can book, cancel, and see their appointments and have a more flexible and controlled interaction with their healthcare (Kosalairaman T et al., 2025). Access to their daily schedule and patient list are availed to doctors allowing them to manage their time and plan their clinical activities well. Administrators will handle the users of the system as well as keep track of the activity in the system as a whole by monitoring the summary reports.
The basic functionalities provided by HAMS are booking of appointments, preventing conflicts, canceling appointments and updating status, seeing the schedule, and basic user management. The system will decrease errors and enhance transparency by distinctly separating roles in the user positions and automating the most important scheduling processes. The main purpose of the HAMS is to offer a credible, sustainable and scalable solution to the issue of organizing hospital appointments effectively.
Appendices
Appendix A: Screenshots of system execution
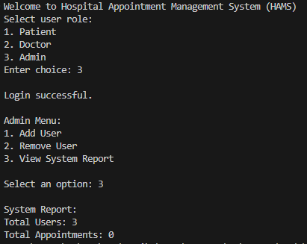
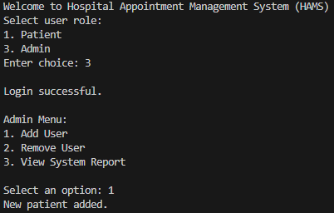
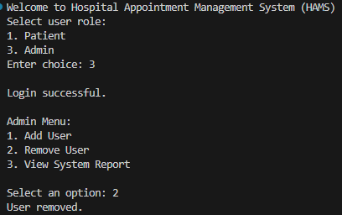
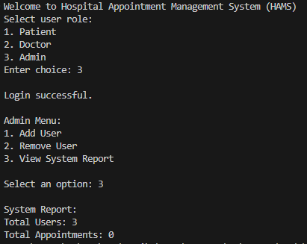
Figure 1: Output Screenshots
Appendix B: Test case table
Table 1: Test Case Table
|
Test Case ID |
Role |
Action Tested |
Input |
Expected Output |
Actual Output |
Result |
|
TC01 |
Patient |
Book Appointment |
Patient → Book |
Appointment booked successfully |
Appointment booked successfully |
Pass |
|
TC02 |
Patient |
Double Booking |
Same date & time |
Conflict detected |
Conflict detected |
Pass |
|
TC03 |
Patient |
Cancel Appointment |
Cancel option |
Status updated to CANCELLED |
CANCELLED shown |
Pass |
|
TC04 |
Patient |
View Appointments |
View option |
Appointments displayed |
Displayed correctly |
Pass |
|
TC05 |
Doctor |
View Daily Schedule |
Doctor → View |
Schedule displayed |
No appointments scheduled |
Pass |
|
TC06 |
Doctor |
View Patient List |
Doctor → Patients |
List of patients |
Alice displayed |
Pass |
|
TC07 |
Admin |
Add User |
Admin → Add |
User added |
New patient added |
Pass |
|
TC08 |
Admin |
Remove User |
Admin → Remove |
User removed |
User removed |
Pass |
|
TC09 |
Admin |
System Report |
View report |
User & appointment count |
Correct values shown |
Pass |
|
TC10 |
Input Validation |
Invalid role |
Role = 4 |
Error message |
Invalid role selected |
Pass |
Appendix C: Code excerpts
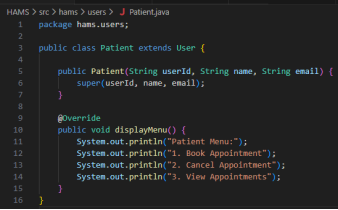
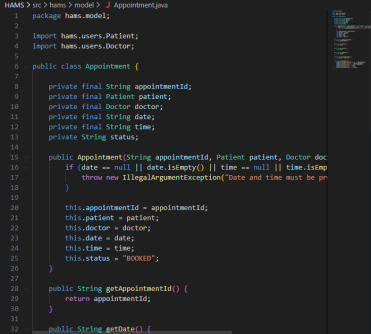
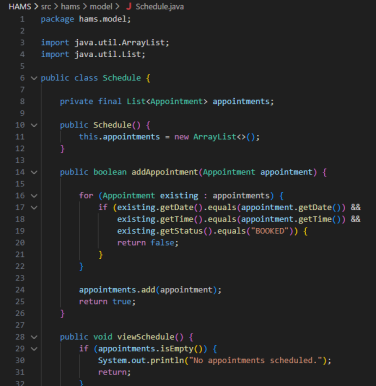
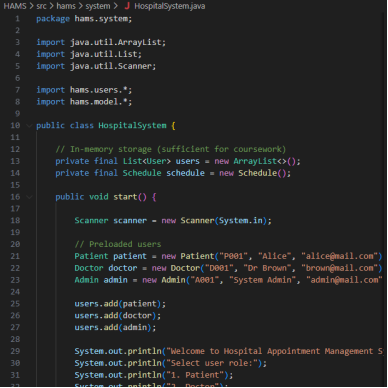
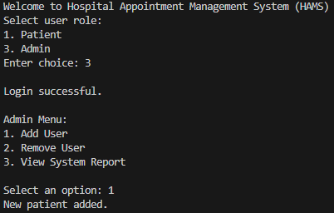
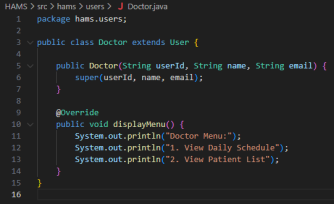
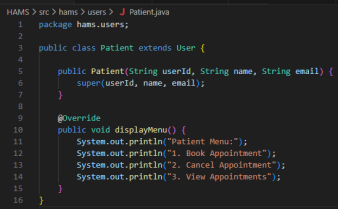
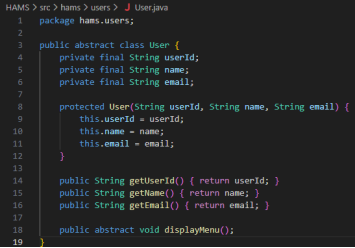 Figure 2: Code Snippets
Figure 2: Code Snippets
Impact of Object-Oriented Programming on HAMS
The object-oriented programming has a key role in the design and implementation of the Hospital Appointment Management System (HAMS) because it directly affects the reliability of the system, its clarity, and extensibility (Simeon and Promise Nlerum, 2024). The use of each principle of OOP is clearly implemented in the system to meet the functional and structural requirements.
1 Encapsulation
To obtain encapsulation, all the class attributes are declared private, and only access by public methods is offered. The User class has attributes like userId, name, and email, which are secured by the use of the private access modifiers and can be accessed by getter methods (Stalin David et al., 2022). The same applies to the Appointment class, which packages sensitive information such as the appointment identifiers, the date, time, and status of the appointment, and can be manipulated by means of controlled manipulation such as cancelAppointment() etc. The Schedule class wraps the list of the appointments and only reveals it through the specific methods such as addAppointment() and getAppointments(). This method will guard integrity of data, discourage unauthorised alteration, and fulfill a state change inside the system will be reasoned by reliable logic.
2 Abstraction
The method of abstraction is realized with the help of the abstract User class that determines shared characteristics and behaviours that all user roles have in common. The abstract method displayMenu() applies a uniform interface and leaves each role to give its implementation. The design conceals complexity of the internal system to the user and allows system interaction on the high level, making system use and development simpler (Royce et al., 2025).
3 Inheritance
The concept of inheritance is used to extend the User class to Patient, Doctor and Admin subclasses. This minimises the number of times a code is duplicated by enabling shared attributes and methods to be declared in the parent class. These features are inherited in each subclass and role-specific behaviour is added, aiding the reuse of code and enhancing maintainability (Menolli and Strik, 2025).
4 Polymorphism
Polymorphism is illustrated by displayMenu() method that is different in its behaviour with the different runtime types of a user. The system will dynamically execute the necessary role-specific menu by invoking this method using a User reference which will lead to cleaner logic and flexible role handling.

DEADLINE TOO
CLOSE?
Get Assignments
Delivered in 3 Hours
Benefits of Using OOP in HAMS Development
The implementation of the Object-Oriented Programming in designing the Hospital Appointment Management System provide a number of practical advantages which automatically improve the quality and reliability of the system. Modularity is one of the most important benefits of the system whereby it is partitioned into well-defined classes like User, Appointment, and Schedule (Ajinkya Kunjir, 2024). This isolation enables drying out of individual components, testing them, and contributing to their refinement without the threat of unforeseen errors in a system.
OOP enhances maintenance also by ensuring that there is a good organisation of the code and reuse. It is possible to make changes to all of the functionality shared by the system, e.g. user attributes or the processing of reservations, without impacting on other unrelated parts. It is especially crucial in healthcare systems, where it might be necessary to make regular updates to satisfy regulatory or operational shifts. The object-oriented design allows new roles, features, or services to be added with very little disruption to the existing code, and has been shown to support the system growing over time.
Also, the readability is improved by meaningful class names and definite method responsibilities, minimizing the number of mistakes in the development process and easing the debugging process. The system is also poised to scale in the future including inclusion of database, graphical user interface or authentication system. All these advantages will result in better healthcare reliability, system accuracy and a lower risk of scheduling and data management mistakes.
Reliable assignment writing service with on-time delivery.
System Design Using UML Diagrams
The design and visualisation of the Hospital Appointment Management System (HAMS) was supported with the help of Unified Modelling Language (UML). UML diagrams give a clear picture on system structure, behaviour, and interactions, which make certain that the system design and implementation are always aligned (Warnett and Zdun, 2024). This strategy was especially effective in dealing with complexity of the system and justification of object-oriented design choice.
1 UML Class Diagram
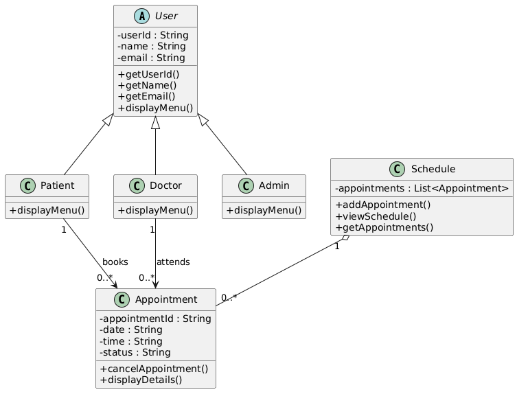
The UML Class Diagram (Figure 5.1) demonstrates the static system structure, comprising of the key classes, attributes, methods, and relationships of the classes. The inheritance structure is defined in the diagram that shows that the abstract User category is the parent of the Patient, Doctor, and Admin categories (Evangelista et al., 2023). This structure has shown good reuse of codes and separation of roles. Associations of Patient, Doctor, and Appointment refer to the real-world associations whereas the aggregation of Schedule and Appointment shows that there is a schedule that contains a number of appointments. The class diagram also played a significant role in making sure that the responsibilities were properly distributed and that the system was based on proper object-oriented principles.
2 UML Sequence Diagram
The UML Sequence Diagram (Figure 5.2) is devoted to the process of booking an appointment with a patient. It draws the chronologic relationship among the Patient, HospitalSystem, Schedule and Appointment objects. The diagram illustrates the flow of the booking request, the creation of an appointment object and the process of the system verifying the existence of scheduling conflicts before the confirmation or rejection of the booking. The diagram was useful in testing the runtime behaviour and correcting the message flow between the objects.
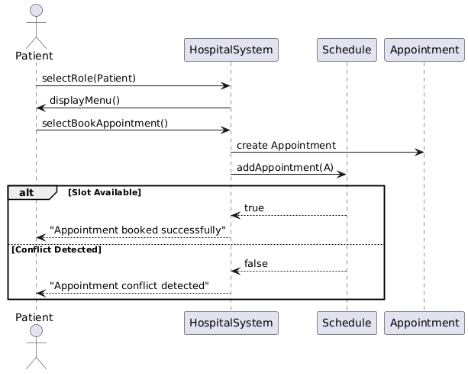 Figure 4: Sequence Diagram
Figure 4: Sequence Diagram
3 UML Activity Diagram
Figure 5.3 (UML Activity Diagram) is the general workflow of the system, which begins with the roles selection and continues with role-related actions. Decision points show various user routes, patient, doctor and admin operation. The diagram helped in the visualisation of the system flow, definition of logical conditions and facilitating effective presentation of the system behaviour to technical and non-technical stakeholders.
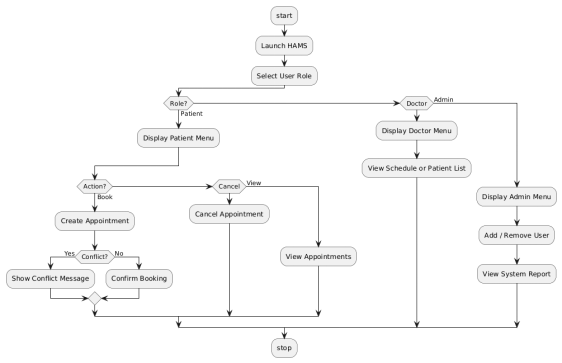 Figure 5: Activity Diagram
Figure 5: Activity Diagram
System Implementation and Key Functionalities
The system implemented is Hospital Appointment Management System (HAMS) which is a console based Java application on an object-oriented architecture. The system is based on role-based access control where users would be operating within the system based on their assigned role: Patient, Doctor, or Admin (Ur et al., 2023). The system is dynamically brought out to show role-specific menus on a per user login using polymorphism; therefore, users are only allowed to access those functionalities they are supposed to have.
Patients will have fundamental appointment management services. They are able to make appointments, with date and time being validated by the system and schedule conflicts being avoided by the Schedule class. They also allow the patients to cancel the appointment which changes the appointment status of BOOKED to CANCELLED without deleting the record so that accurate history of the appointment can be tracked. Also, patients will have an opportunity to see their appointments which is easy to access and transparent.
Physicians can view operational data only in a read-only form. They are able to see their day-to-day schedule, where all the appointments in the schedule are shown including those that have been cancelled and see a list of patients, which helps in clinical planning and managing workload. The administrators take care of system configuration and oversight. They are able to add users, delete users and see a system report reflecting an overview of the number of users and appointments.
The overlapping appointment slots are also checked whereby the validation of a booking is also done through conflict prevention logic (Kothiya, 2025). Status updates are explicit to control the appointment lifecycle, and enhance reliability and traceability. The use of console-based design was driven by the desire to ensure ease of understanding and concentrate on the essence of logic and in-memory storage is valid since it is a functional prototype without the inclusion of databases.
Advanced plagiarism checker UK with detailed reports.
Testing and Validation
1 Testing Approach
The testing was done under a functional black-box testing mode whereby various user roles (Patient, Doctor, and Admin) were tested with predetermined inputs to test the behaviour of the system. The core features such as booking appointments, conflict prevention, cancellation, schedule viewing, and management of the administrative users were tested with regard to their anticipated results. This system was run several times to test robustness, input validation and error handling. The console outputs were recorded as the evidence of proper execution and all tests were judged on the issues of whether the obtained output corresponded to the expected one.
2 Test Case Summary
They came up with a full suite of test cases, and ran them, as summarised in the testing table (see Appendix A). These tests were on successful appointment booking, conflicts of double-booking, and appointment cancellation with status indication, and the most important administrative functions including user management and system reporting (Zhou et al., 2023). The outputs were all of the expected results in all the test cases.
3 Validation Outcome
The results of the testing prove that the Hospital Appointment Management System is acting as expected. Every functional element worked well, mishaps were managed and the system was found to run steadily. These results show that the system is stable, logically designed, and appropriate as a prototype healthcare appointment management solution.
Critical Reflection
The preparation of the Hospital Appointment Management System was a great experience in learning the practical use of Object-Oriented Programming beyond theory. This project made me realize even better that the principles of OOP can help shape the model of real-life systems, specifically, in a healthcare environment, where precision and division of roles are vital (Kachavimath et al., 2017). The application of encapsulation, inheritance, abstraction, and polymorphism in a working system facilitated the need to structure classes in terms of distinct responsibilities as opposed to the functionality aspect.
Main challenge that I faced was dealing with system state, especially in dealing with appointment status change and consistency in the behavior of cancellations and conflict detection. The associations between the classes also had to be carefully designed, particularly with regard to how Schedule was to interrelate with the Appointment objects without necessarily binding them closely. These delays motivated a careful system design at the outset.
One strategy which proved quite effective was incremental development, in which core logic was developed and tested first, and user interaction functionality added subsequently. Moreover, the use of UML-first design method allowed to visualise relationships and workflow decreasing implementation errors. With increased time, I would enhance the system to allow persistent data storage, graphical user interface, and more security control features like authentication, access control to better represent real-life healthcare systems.
Discussion and Future Enhancements
Although the Hospital Appointment Management System is effective in illustrating the principal concepts of object-oriented and functional requirements, a number of limitations are observable owing to the prototype form. The system is based on in-memory storage and hence is not integrated with database, that is, all the information is lost on the termination of the application (Dreseler, 2022). Moreover, the user interface is a console interface that restricts the usability and accessibility to the non-technical users. Another limitation of the system that can lead to restricted enforcing secure access control is the lack of any authentication mechanisms, which is an essential aspect of healthcare environments.
Ethically and practically, healthcare systems are required to emphasise the availability, integrity, and confidentiality of data. Patient data is very sensitive and any actual implementation would have to be in accordance to data protection laws and implement a very strict access control policy. One improvement that can be made in the future is the inclusion of a relational database that will allow persistent storage, the addition of a graphical or web-based interface that will be easier to use, and role-based authentication that will help to prevent unauthorized access into the system. Moreover, the audit logging may be introduced to monitor the users and improve accountability and promote safer and more transparent healthcare operations.
Read Related samples -Predicting Response to First Pharmacotherapy Treatment in Lung Cancer Patients Using Machine Learning
Conclusion
The Hospital Appointment Management System evolved as a way of having an organized and effective way to address medical appointments with the use of Object-Oriented Programming concepts. OOP was found to be successful in developing a maintainable, reliable, and modular system that reflects the real-life healthcare process and role. There was a successful completion of all the system objectives such as role-based access, lifecycle management of appointments and prevention of conflicts. Overall, the system has the high quality of design and offers a solid base to proceed with the further development into the full-fledged healthcare management system.
References
- Ajinkya Kunjir (2024). Exploring the Applications of Complex Adaptive Systems in the Real World: A Review. Benthamdirect.com, [online] pp.136-160. Available at: https://www.benthamdirect.com/content/books/9789815179606.chapter-7.
- Dreseler, M. (2022). Automatic tiering for in-memory database systems. Uni-potsdam.de. [online] doi:https://doi.org/10.25932/publishup-55825.
- Evangelista, J.E., Clarke, D.J.B., Xie, Z., Marino, G.B., Utti, V., Jenkins, S.L., Ahooyi, T.M., Bologa, C.G., Yang, J.J., Binder, J.L., Kumar, P., Lambert, C.G., Grethe, J.S., Wenger, E., Taylor, D., Oprea, T.I., de Bono, B. and Ma'ayan, A. (2023). Toxicology knowledge graph for structural birth defects. Communications Medicine, [online] 3(1), pp.1-14. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43856-023-00329-2.
- Hasan, M. (2025). Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) as the Optimal Paradigm for Microservice Architectures: A Comprehensive Analysis. [online] Academia.edu. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/download/120678728/OOP_as_the_Optimal_Paradigm_for_Microservice_Architectures_A_Comprehensive_Analysis.pdf.
- Kachavimath, A.V., Deepa Mulimani, Seeri, S.V. and Patil, P.R. (2017). Object Oriented Programming Using Real Life Paradigm with Open Source Technology. Journal of Engineering Education/Journal of engineering education transformations/Journal of engineering education transformation. doi:https://doi.org/10.16920/jeet/2017/v0i0/111814.
- Kosalairaman T, Maalini D, Kiruthika R, Janani SK, Nithya T and Pavithra P (2025). Smart Health Consulting and Appointment Booking System with Real-Time Scheduling and Patient-Doctor Communication. [online] pp.1-6. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/aimla63829.2025.11040602.
- Kothiya, B. (2025). Market analysis of an appointment booking system : understanding market demand and innovation in appointment scheduling systems. Theseus.fi. [online] doi:http://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/895046.
- Menolli, A. and Strik, B. (2025). Educational Insights from Code: Mapping Learning Challenges in Object-Oriented Programming through Code-Based Evidence. [online] arXiv.org. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.17743 [Accessed 12 Jan. 2026].
- Royce, R., Kaufmann, M., Becktor, J., Moon, S., Carpenter, K., Pak, K., Towler, A., Thakker, R. and Khattak, S. (2025). Enabling Novel Mission Operations and Interactions with ROSA: The Robot Operating System Agent. [online] pp.1-16. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/aero63441.2025.11068426.
- Simeon, I.-E. and Promise Nlerum (2024). Design and Development of a Medical Appointment and Evaluation Management Model. [online] doi:https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5061729.
- Stalin David, D., Anam, M., Kaliappan, C., Arun Mozhi Selvi, S., Kumar Sharma, D., Dadheech, P. and Sengan, S. (2022). Cloud Security Service for Identifying Unauthorized User Behaviour. Computers, Materials & Continua, 70(2), pp.2581-2600. doi:https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2022.020213.
- Ur, A., Mahmood, T., Saba, T., Saeed Omer Bahaj, Alamri, F.S., Muhammad Waseem Iqbal and Khan, A.R. (2023). An Optimized Role-Based Access Control Using Trust Mechanism in E-Health Cloud Environment. IEEE Access, 11, pp.138813-138826. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3335984.
- Warnett, S.J. and Zdun, U. (2024). On the Understandability of MLOps System Architectures. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 50(5), pp.1015-1039. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/tse.2024.3367488.
- Zhou, Y., Viswanatha, A., Motaleb, A.A., Lamichhane, P., Chen, K.-Y., Young, R., Gurses, A.P. and Xiao, Y. (2023). A predictive decision analytics approach for primary care operations management: A case study of double-booking strategy design and evaluation. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 177, p.109069. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2023.109069.



 Company
Company


















